Among all MCPCBs,aluminum PCB is one of the most common types.The base material of an aluminum-based PCB consists of an aluminum core and standard FR4,which offers efficient heat dissipation and cools electronic components,thereby improving the overall performance of the product.
Environmental friendly:Aluminum is non-toxic and recyclable. Its production promotes energy conservation and is easy to assemble.Also,using aluminum as the base material for PCBs contributes to environmental protection.
Excellent heat dissipation:High temperatures can cause severe damage to electronic devices. Therefore,using materials that facilitate heat dissipation is the right choice.Aluminum effectively transfers heat away from heat-generating components or important parts, minimizing any potentially harmful impact on the circuit board.
Durability:Aluminum provides strength, toughness,and durability that ceramic or glass fiber substrates cannot offer.Aluminum is a hard material that reduces the risk of accidental damage during production,handling,and everyday use.
Lightweight:Aluminum enhances the strength and resilience of products without adding any significant extra weight.
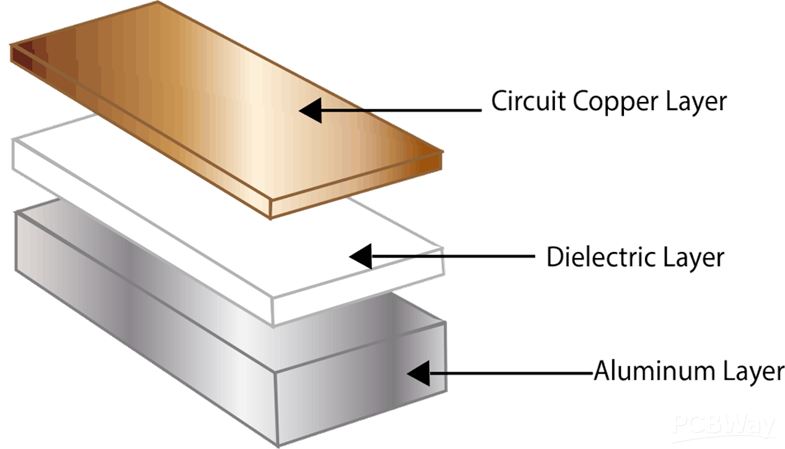
Circuit Copper Layer:The copper circuit layer (typically using electrolytic copper foil) is etched to form the printed circuit, which is used for component assembly and connections.Compared to traditional FR4,aluminum PCBs can carry higher currents for the same thickness and line width.
Dielectric insulation Layer:The dielectric insulation layer is a core technology of aluminum PCBs, primarily serving the purposes of bonding, insulation, and thermal conduction. A better thermal conductivity of the insulation layer helps in dissipating the heat generated by components. Lower working temperatures of the devices increase power loading, reduce volume, extend lifespan, and enhance power output.
Metal Substrate: The choice of metal for the insulated metal substrate depends on various factors such as thermal expansion coefficient, thermal conductivity, strength, hardness, weight, surface condition, and cost of the metal substrate.
In general, considering cost and technical performance, aluminum substrates are the preferred choice. Available aluminum materials include 6061, 2052, 1060, etc. If there are higher requirements for thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, electrical properties, or other specific performance criteria, copper, stainless steel, iron, or silicon steel plates can also be used.
One-layer aluminum PCB with single component mounting side

One-layer aluminum PCB with a single component mounting side has the simplest structure and is also the easiest to manufacture. The circuit is directly etched on the copper layer of the aluminum laminate board.
Heat is transferred from the components to the copper layer,to the PP layer,then to the aluminum layer.
Two-layer aluminum PCB with single component mounting side

Two-layer aluminum PCB with a single component mounting side has two copper layers and PP layers.
Heat is transferred from the components to the first copper layer, to the first PP layer,to the second copper layer,to the second PP layer and then to the aluminum layer.
Two-layer aluminum PCB with dual component-mounting sides

When single-sided PCBs are unable to accommodate all the circuitry, aluminum PCBs can be designed as double-sided. The structure of a two-layer aluminum PCB with dual component-mounting sides is similar to that of a two-layer FR4 PCB with dual component-mounting sides. However, the space between PTHs and the aluminum base is filled with resin.
Heat is transferred from the components to the copper layer, then to the PP layer, and finally to the aluminum layer.
Four-layer aluminum PCB with dual component-mounting sides

A four-layer aluminum board has two copper layers and PP layers.
Heat is transferred from the components to the outer copper layer, then to the first PP layer, further to the second copper layer, then to the second PP layer, and finally to the aluminum layer. Therefore, the thermal conductivity of a four-layer PCB is lower than that of a single-layer PCB and a two-layer aluminum PCB with dual component-mounting sides.
Audio Equipment: input amplifier, output amplifier, balanced amplifier, audio amplifier, preamplifier, power amplifier.
Power Supply: switch regulator, DC/AC converter, SW regulator, etc.
Communication Electronic Devices: high-frequency amplifier, filtering device, transmission circuit.
Office Automation Equipment: motor driver, etc.
Automobiles: electronic regulator, ignition system, power controller, etc.
Computers: CPU board, floppy drive, power supplies, etc.
Power Modules: inverter, solid-state relay, rectifier.
Lamps and Lighting: With the promotion of energy-saving lamps, various colorful LED energy-saving lamps are highly welcomed in the market, and aluminum PCBs used in LED lamps are being widely used.

2 layers aluminum PCB substrate, copper thickness 1oz, aluminum base on the bottom of the laminate is probably like this for reference. The above parameters are basically unchanged. The thickness of the aluminum base is the thickness of the plate selected by the customer minus the thicknesses above.
Aluminum PCBs are typically stored in a dark and dry environment. Most aluminum PCBs are prone to moisture absorption, yellowing, and darkening. Generally, they should be used within 48 hours after being unsealed.
We currently support aluminum bases from BOYU, CSEM and GDM with thermal conductivity of 1.0~3.0W/m·k.

By the way:
If we place an order for the wireless circuit of single-sided aluminum substrate, it is best to note whether or not to add thermal conductive glue, otherwise PCBWay will confirm with you whether thermal conductive glue is needed. The thermal conductive glue is milky white. The white part in the picture.

More information check here: